Subscribe
Be the first to know about our latest posts.
Explore Icreon’s Digital Product Development Services
Dissecting CMS and Exploring its Latest Types
In this digital age, Content Management Systems (CMS) play a pivotal role in simplifying website and content management. Whether you're a seasoned web developer or a business owner seeking to optimize your online presence, this guide will navigate you through the world of CMS. Discover the diverse types, functionalities, and benefits of CMS platforms, and learn how to leverage their power to create, edit, and manage content effortlessly.
What is a Content Management System?
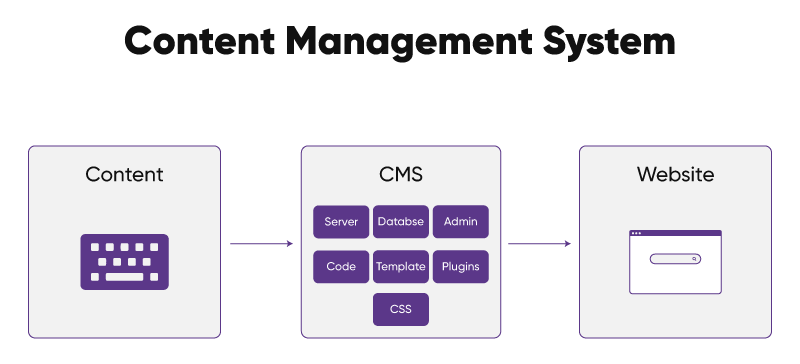
A content management system, or CMS for short, is a piece of software that enables users to make changes to websites without having to worry about coding. You can efficiently administer a website using a CMS without having to be an expert coder. Instead of using coding, you can download and buy extensions to alter the look and feel of your website. The same tool can accommodate numerous users working on its backend.
For content creation purposes, most CMS platforms provide a WYSIWYG editor, which stands for ‘what you see is what you get’. WYSIWYG editors empower content creators to design and format posts and pages effortlessly, eliminating the need for coding. With a real-time preview, the content appears exactly as it will be on the live website.
Curious how one system can do all of this? Let’s break it down.
Two Core Parts of a CMS
A CMS consists of two parts: a CMA (content management application) and a CDA (content delivery application)
Content Management Application: The Content Management Application is the user-facing part of a CMS where content administrators and editors interact with the system. It provides an intuitive and user-friendly interface often equipped with a WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) editor. This editor allows users to create, edit, format, and organize content without the need for extensive technical knowledge. Content administrators can easily add text, images, videos, links, calls to action (CTAs), and other multimedia elements to web pages. It simplifies the content creation process, making it accessible to individuals without coding expertise. In essence, the CMA empowers content creators to focus on the substance of the content rather than the technical intricacies.
Content Delivery Application: On the other hand, the Content Delivery Application, often referred to as the backend or server-side component of the CMS, plays a pivotal role in storing and delivering content to the website or application. It's responsible for managing the database where content is stored, organizing it, and ensuring its availability to be presented to users when they access a website or application. The CDA responds to user requests, retrieves the relevant content from the database, and dynamically generates web pages for display. It ensures that the content is delivered to the end-users seamlessly and efficiently. This separation of content creation (CMA) and content delivery (CDA) allows for content to be updated, managed, and presented independently, providing a flexible and scalable approach to website and application management.
Why Do You Need A Content Management System?
Content management simplifies creating, organizing, and publishing digital content, benefiting businesses of all sizes. It also ensures that your content remains accurate, up-to-date, and aligned with your company's marketing objectives. The ultimate goal is to deliver valuable and useful digital content to your audience while staying focused on achieving your business goals. With effective content management, you can optimize your content's value and enhance its relevance to your target audience.
Let’s explore some of its important benefits.
Related Article: How to rejuvenate content strategy with effective ECM
Enhanced User Experience
In the digital realm, the user experience is king.
With customizable themes and templates, you can design an attractive website that aligns perfectly with your brand's identity, resulting in increased user engagement and higher customer satisfaction.
Streamlined Collaboration and Workflow
A CMS streamlines collaboration efforts for businesses and organizations with multiple content creators. It enables team members to work simultaneously on different aspects of the website, providing a smooth and organized workflow. Administrators can assign roles and permissions, granting specific access to designated individuals, ensuring security and accountability.
Advanced Plug-ins and Functionalities
A vast array of plugins and add-ons are available for most CMS platforms, allowing you to extend your website's functionalities without coding expertise. Whether you want to integrate social media sharing buttons, set up an e-commerce store, or implement contact forms, CMS plugins make it possible with minimal effort.
Scalability and Flexibility
CMS platforms offer scalability, accommodating your website's expansion without a hitch. Whether you want to add new pages, integrate key features, or increase server capacity, a CMS makes scaling your website a breeze, future-proofing your online presence.
Overall, the benefits of CMS are highly impactful. From simplifying content creation and streamlining collaboration, a CMS empowers you to unleash the full potential of your website. Now that we’ve outlined the benefits of CMS and how they’re a crucial part of a modern website, it’s time to highlight the CMS solutions on the market. One of the most common solutions on the market is the traditional CMS architecture that is paired with coupled CMS.
Different Types of CMS
There are different types of CMSs. Each CMS comes with unique features, capabilities and caters to specific user needs. To better grasp the features and applications of several common CMS categories, let's explore:
Related Article: SaaS vs On-premises CMS
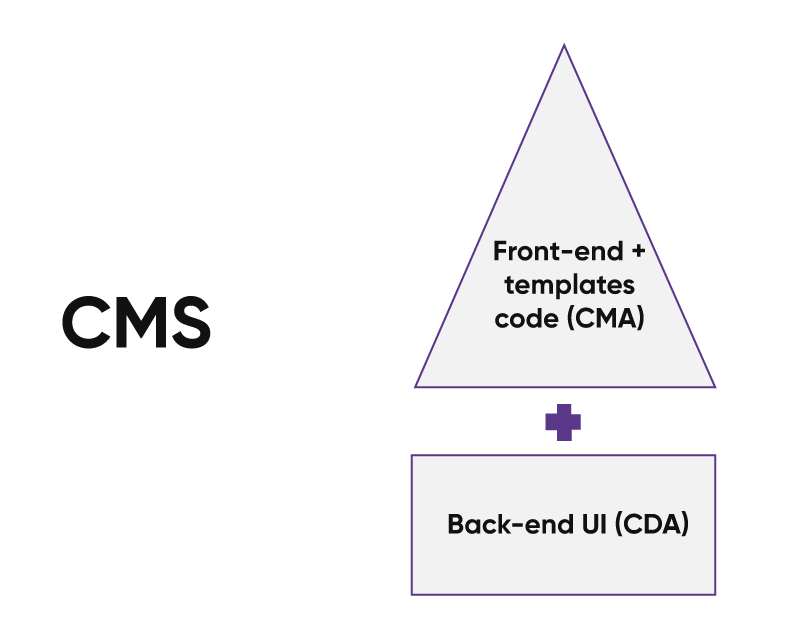
Coupled CMS
A coupled CMS, also known as a traditional or monolithic CMS, is a type of content management system where the backend (content management) and the front-end (presentation layer) are tightly integrated.
The content is created and stored in a database within the CMS backend in a coupled CMS architecture. When a user requests a webpage, the CMS retrieves the content from the database and combines it with the website's templates and layout to generate the final HTML output. The user's web browser will subsequently receive this HTML output for display.
The diagram below represents the architecture of a coupled CMS:
While coupled CMS platforms offer simplicity and ease of use, they may not be ideal for projects that require highly customized front ends, integration with multiple platforms, or the ability to deliver content to various channels and devices. Decoupled architectures or headless CMS may be more suitable, as they provide greater flexibility and freedom for front-end development and content delivery. WordPress and Drupal are excellent examples of Coupled CMS architecture.
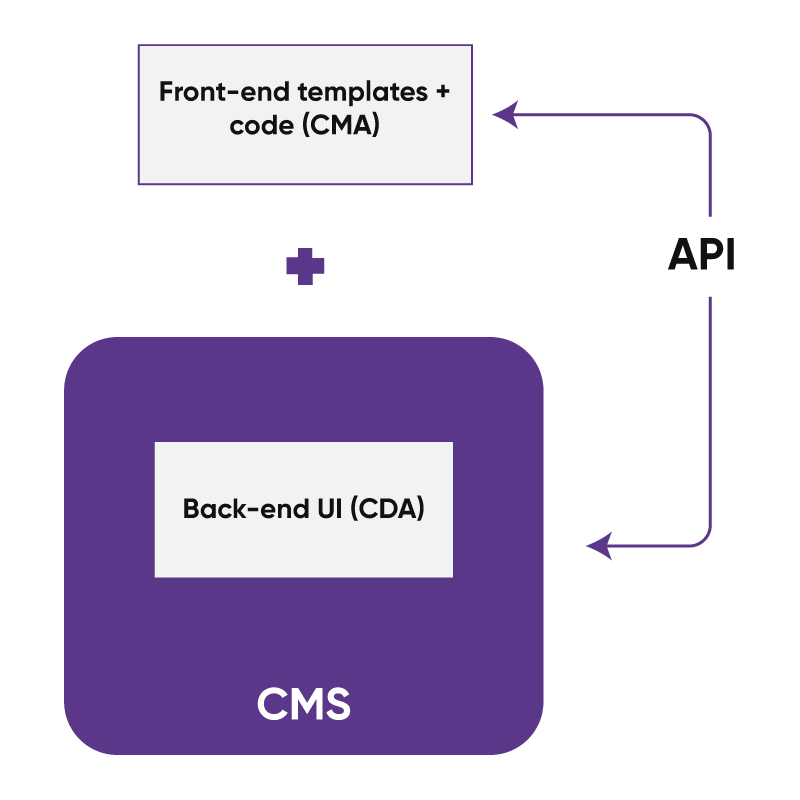
Decoupled CMS
Decoupled architecture provides greater flexibility compared to coupled CMS. Faster launch times are obtained as a result of the concurrent updates and simpler maintenance made possible by this separation. A decoupled CMS makes deployment easier and relies less on the development team to provide new features. Some widely popular examples of decoupled architecture are Sitecore and Episerver. However, Drupal and WordPress are providing their extensions and plugins to provide decouple sort of functionalities.
The below image depicts the structure of a decoupled CMS:
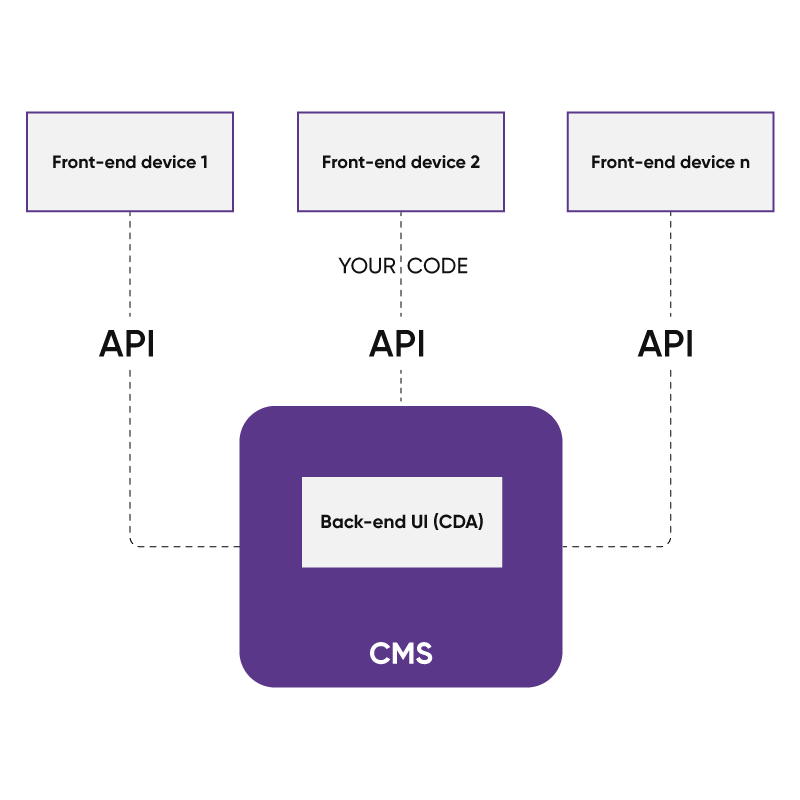
Headless CMS
Headless CMS separates the backend content management from the front-end presentation, offering enhanced flexibility and personalization. Content is stored and managed in the backend and delivered to the front-end through APIs.
As your website or application grows, the backend CMS infrastructure can handle increased traffic and content updates without affecting the front-end performance. With the growing demand for personalized and seamless user experiences, headless CMS is becoming an increasingly attractive option for forward-thinking organizations looking to stay at the cutting edge of web development and content delivery. Some popular headless CMS examples include Contentstack, Storyblok, Contentful, etc.
The below diagram shows a logical overview of the overall architecture:
Must Read: Learn how to future-proof your business with headless CMS.
Hybrid CMS
The newest CMS, the hybrid model, has been made possible by decoupled and headless architectures. Hybrid CMS solutions enable you to mix and match between headless and traditional delivery methods. This flexibility optimizes the user experience based on the content requirements. With its seamless integration, enhanced security, and scalability, hybrid CMS is an attractive solution for organizations seeking the best of both worlds in a rapidly evolving digital landscape. Some popular Hybrid CMS examples include Bloomreach, Core dna, Sitecore, Kentico, and more.
SaaS CMS
Lastly, there are SaaS-based content management systems. doesn't need to be set up, installed, or hosted on a server that has already been configured.
A SaaS-based CMS is an excellent solution if you need a straightforward web presence, as it offers intuitive interfaces and straightforward setups, making them accessible to non-technical users. Additionally, the ease of SaaS CMS enables businesses to manage and update their website content with minimal training or technical expertise. Examples of SaaS-based CMS categories are Magento, CMS Hub, Shopify, PrestaShop, WordPress, Wix, and more.
Must Read: Sitecore vs Drupal: A Spectrum of Capabilities to Reimagine Content Mangement
Conclusion
While the CMS landscape is diverse, selecting the right content management system is crucial for the success of your business. There are several ways to assess whether a content management system will suit your organization well. You should avoid an outdated CMS interface, as it will be harder for users to navigate. Additionally, by choosing a CMS with an added layer of security, things will likely run more smoothly. Ultimately, when choosing your CMS, choose wisely by taking the time to research and evaluate your needs.
To know more about which CMS best suits your business needs, start a conversation with our CX Experts.